Description
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Klonopin (Clonazepam) B. Purpose of article C. Overview of article
II. What is Klonopin (Clonazepam)?
A. Description of medication B. Medical uses C. Mechanism of action D. Dosage and administration
III. Effects of Klonopin (Clonazepam)
A. Therapeutic effects B. Side effects C. Risks and precautions D. Addiction potential
IV. Medical Conditions Treated with Klonopin (Clonazepam)
A. Anxiety disorders 1. Generalized anxiety disorder 2. Panic disorder 3. Social anxiety disorder B. Seizure disorders 1. Epilepsy 2. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome C. Sleep disorders 1. Insomnia 2. Sleep apnea 3. Restless leg syndrome
V. Withdrawal from Klonopin (Clonazepam)
A. Symptoms of withdrawal B. Withdrawal timeline C. Risks and complications of withdrawal D. Management of withdrawal
VI. Alternatives to Klonopin (Clonazepam)
A. Non-pharmacological treatments 1. Cognitive-behavioral therapy 2. Mindfulness meditation 3. Exercise B. Pharmacological alternatives 1. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) 2. Benzodiazepine receptor agonists (BzRAs) 3. Antidepressants
VII. Conclusion A. Summary of article
B. Implications for patients and healthcare providers C. Future research directions
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Klonopin (Clonazepam)
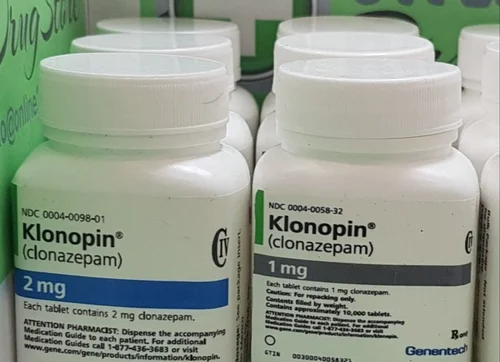
Klonopin (Clonazepam) is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as benzodiazepines. It is primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, seizure disorders, and sleep disorders.
B. Purpose of article
The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of Klonopin (Clonazepam), including its medical uses, effects, and potential risks. It will also explore the medical conditions that can be treated with Klonopin, withdrawal from the medication, and alternatives to Klonopin.
C. Overview of article
This article will begin by describing what Klonopin (Clonazepam) is, including its medical uses, mechanism of action, and dosage and administration. It will then explore the therapeutic effects and side effects of Klonopin, as well as the risks and precautions associated with the medication. The article will then discuss the medical conditions that can be treated with Klonopin, including anxiety disorders, seizure disorders, and sleep disorders. Next, the article will examine withdrawal from Klonopin, including the symptoms of withdrawal, withdrawal timeline, and management of withdrawal. Finally, the article will explore alternatives to Klonopin, including non-pharmacological treatments and pharmacological alternatives.
II. What is Klonopin (Clonazepam)?
A. Description of medication
Klonopin (Clonazepam) is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as benzodiazepines. It is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that works by increasing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits the activity of other neurotransmitters in the brain.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.